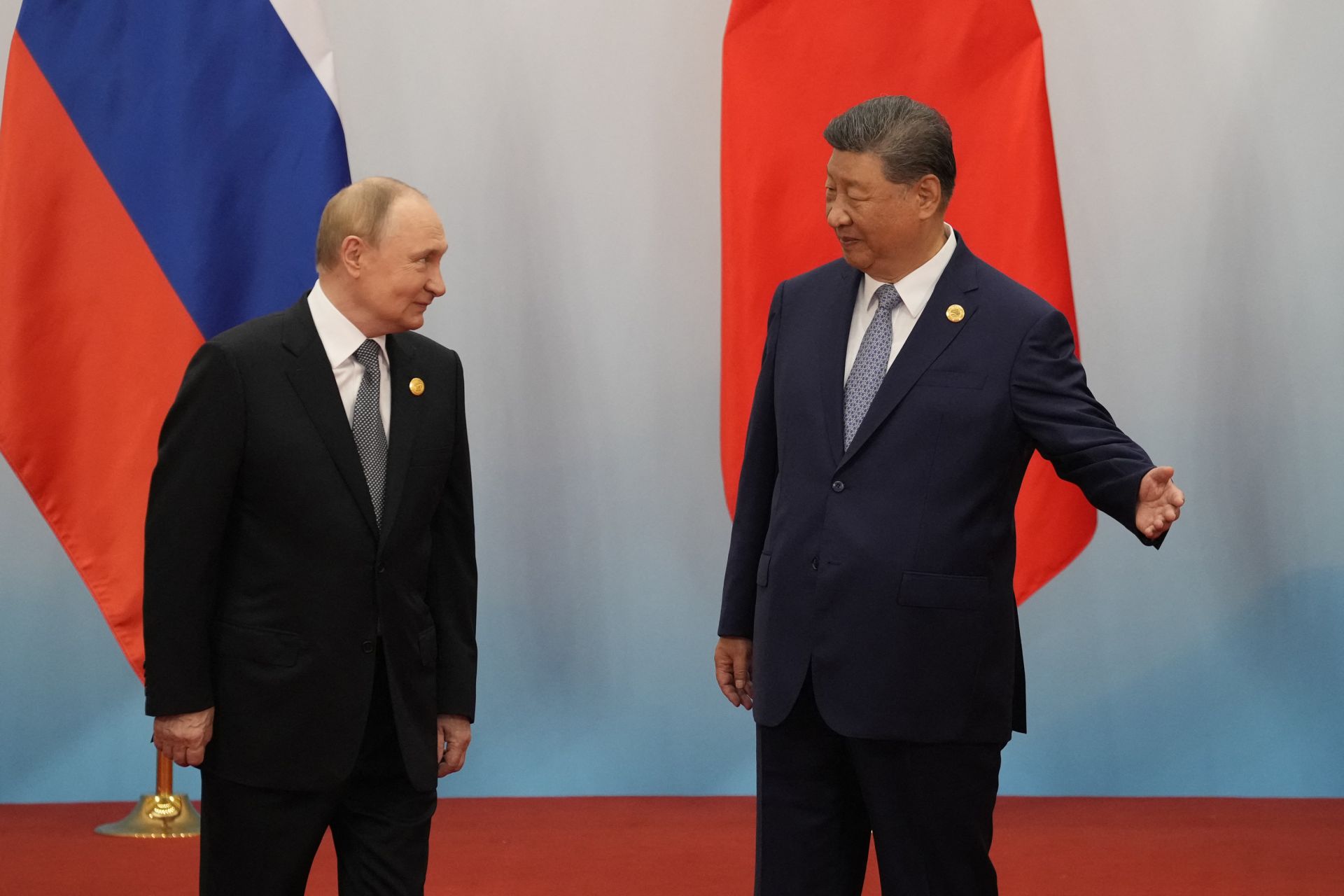
The evolving partnership between Chinese President Xi Jinping and Russian President Vladimir Putin has drawn the attention of the international community. Their growing alignment signals an ambition to present an alternative to the Western-led global order, with both leaders emphasizing strategic cooperation at a time of heightened geopolitical tensions.
This alliance has emerged in the context of increasing tension with the United States and its partners. China’s emergence as a dominant economic and military force, along with Russia’s ongoing opposition to Western strategies, has facilitated more extensive cooperation between these two countries. Their regular joint appearances and reciprocal backing in important global platforms highlight this mutual ambition for a multipolar world.
Observers have commented that the latest meetings between Xi and Putin have underscored a shared interest rather than just a symbolic partnership. Both countries aim to lessen reliance on financial systems controlled by the West, boost trade routes beyond conventional pathways, and increase their influence in areas such as Asia, Africa, and Latin America. These actions indicate a wish to counter what they view as excessive U.S. influence in world matters.
China’s diplomatic positioning has been especially assertive in recent years, projecting itself as a mediator and a proponent of stability while simultaneously increasing its military presence in key areas. The country’s Belt and Road Initiative continues to expand economic connectivity, offering infrastructure investments to developing nations. This strategy serves not only to boost trade but also to enhance China’s political influence across emerging markets, positioning it as a viable alternative to Western institutions.
Russia, on its end, is determined to preserve its significance despite dealing with major sanctions and political seclusion from Western countries. By enhancing its relationship with Beijing, Moscow acquires a crucial ally in commerce and technology, aiding in alleviating the economic impacts of Western limitations. This mutual reliance has intensified since Russia’s participation in the Ukraine conflict, which widened the gap with Europe and the United States.
Both leaders have consistently highlighted the importance of honoring sovereignty and refraining from meddling in domestic matters, positioning themselves in opposition to what they characterize as interventionist approaches by Western countries. This perspective resonates with nations that perceive themselves as marginalized or limited by Western diplomatic influence, thus rendering the China-Russia alliance an attractive choice for those looking for different partnerships.
Energy collaboration continues to be a fundamental aspect of their partnership. Russia has shifted a significant portion of its oil and gas exports to Asian countries, with China becoming one of the biggest purchasers. Pipelines and long-term agreements guarantee a constant supply, enabling Beijing to obtain vital resources for its swiftly expanding economy. This energy connection enhances their interdependence and solidifies the stability of their bond.
Military collaboration is another key dimension. Joint exercises and defense technology exchanges between the two nations have increased significantly, signaling an alignment not only in diplomatic rhetoric but also in strategic capability. While both leaders assert that this cooperation is defensive in nature, analysts suggest it serves as a warning to the West that the global balance of power is shifting.
The significance of Xi and Putin appearing side by side at international gatherings is immense. Their alliance indicates that the time of unquestioned Western leadership could be waning. By aligning their stances on topics like global management, commerce regulations, and resolving disputes, they strive to influence organizations and standards to mirror their own interests and principles.
Despite the growing closeness, challenges persist. China remains cautious about becoming entangled in conflicts that could harm its global trade ambitions, while Russia seeks to avoid a relationship that places it in a subordinate position. The asymmetry in economic power—China being far stronger than Russia—creates a dynamic that requires careful management to maintain mutual benefits without eroding sovereignty.
Western governments view this alignment with concern, interpreting it as a direct challenge to the liberal international order. Sanctions, diplomatic isolation, and military support for allies are some of the measures being employed to counterbalance this emerging axis. However, the resilience of Xi and Putin’s cooperation suggests that this partnership is not a temporary arrangement but a long-term strategy.
The implications of this alliance extend beyond bilateral relations. For countries in Africa, the Middle East, and Latin America, it offers an opportunity to diversify alliances and access alternative sources of investment and security cooperation. As a result, the influence of Western powers in these regions may face gradual erosion, leading to a more fragmented global landscape.
Global organizations and multilateral forums are also likely to experience the effects of this partnership. Both China and Russia have signaled their intention to advocate for reforms in institutions such as the United Nations, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund. By pushing for changes that reflect a multipolar reality, they aim to weaken Western leverage in shaping international norms and economic systems.
From an economic perspective, China’s position as a worldwide production center and its progress in technology fields like artificial intelligence, telecommunications, and sustainable energy grants it considerable influence. Russia offers resources and military knowledge, forming a complementary synergy that furthers their mutual objectives. Together, they aim to establish a network that is more resilient to Western penalties and financial constraints.
The way people view this situation in each nation supports this path. State-controlled outlets in China and Russia often highlight the solidity of their alliance, presenting it as a stabilizing and equitable influence in international relations. This storyline finds a receptive audience at home, enhancing the authority of both governments as protectors of autonomy and liberty in a world they describe as ruled by Western agendas.
As global attention focuses on the growing relationship between Xi and Putin, inquiries emerge regarding the future of global relations. Will this partnership initiate a new period of geopolitical rivalry, or can it harmoniously coexist with Western nations within a balanced structure? The outcome will influence diplomacy, commerce, and security for the coming decades.
One certainty remains: the relationship between China and Russia has evolved from pragmatic cooperation to a strategic partnership with global implications. As they continue to present themselves as champions of a multipolar order, their combined influence is set to reshape the international system, challenging assumptions about who leads and who follows in the 21st century.